Margin trading funding is a crucial aspect of leveraged investing, allowing traders to borrow funds to amplify their positions. While this strategy can enhance potential gains, it also increases risk exposure. Understanding best practices is essential for investors to navigate margin trading funding effectively.
Understanding Margin Trading Funding
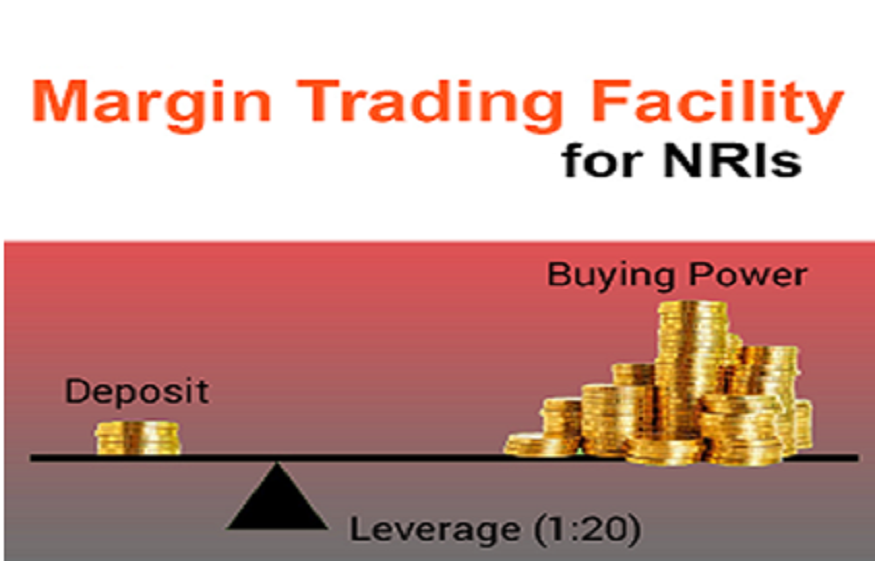
Margin trading funding involves borrowing money from a broker or funding provider to trade assets. Investors use their own capital as collateral, with the borrowed funds magnifying their buying power. Brokers charge interest on borrowed funds, which affects overall profitability.
Best Practices for Investors
- Choose a Reliable Broker
Selecting a reputable broker with transparent margin requirements, competitive interest rates, and robust risk management tools is critical. Look for platforms that offer customizable leverage options and margin call alerts. - Manage Leverage Wisely
High leverage increases profit potential but also amplifies losses. Investors should use leverage conservatively, ensuring they do not overextend their positions. Maintaining a margin-to-equity ratio that aligns with risk tolerance is key. - Monitor Margin Calls and Liquidation Risks
Brokers issue margin calls when an investor’s equity falls below the required maintenance level. Failure to add funds can result in forced liquidation of positions. Regular monitoring of account balances and margin levels helps avoid unexpected losses. - Diversify Investments
Concentrating all funds into a single asset class heightens risk. Diversification across various assets reduces potential downsides and balances portfolio volatility. - Stay Informed on Market Conditions
Margin trading is highly sensitive to market fluctuations. Investors should follow economic trends, interest rate changes, and geopolitical events to anticipate potential price movements.
By applying these best practices, investors can enhance their margin trading experience while mitigating risks and maximizing profitability.
What is a 3-in-1 Demat Account?

A 3-in-1 Demat account integrates a savings account, trading account, and Demat account into one platform, simplifying investments in stocks, mutual funds, and other securities. Leading banks like HDFC, ICICI, and Kotak offer these accounts, making them ideal for seamless trading.
Key Factors to Consider
1. Brokerage and Transaction Fees
Compare brokerage rates across providers. Some banks charge a flat fee, while others follow a percentage-based model. Choose one that aligns with your trading frequency.
2. Ease of Use and Trading Platforms
A well-designed mobile app and web platform enhance your trading experience. Look for real-time market data, charting tools, and easy order execution.
3. Account Opening and Maintenance Charges
Banks charge fees for opening and maintaining a 3-in-1 account. Some providers offer zero or discounted AMC (Annual Maintenance Charges), which can be beneficial.
4. Banking Integration and Fund Transfers
A smooth fund transfer process between the savings and trading account is crucial. Instant transfers reduce delays, helping you take advantage of market opportunities.
5. Research and Advisory Services
Many banks offer investment research, stock recommendations, and market analysis. If you need guidance, choose a provider with strong research support.
Final Thoughts
Your best 3 in 1 Demat account depends on your trading style, cost preferences, and platform usability. Compare multiple banks before making a decision to ensure a hassle-free investment journey.


















+ There are no comments
Add yours